Article Outline
TOC
Collection Outline
一、实现二叉树的先序、中序、后序遍历
二叉树的示例结构为:
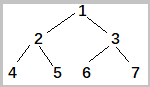
实际函数访问结点的顺序为:1 2 4 4 4 2 5 5 5 2 1 3 6 6 6 3 7 7 7 3 1 结束
(一)使用递归的方式
以先序遍历二叉树为例,可以发现递归方式==首先尝试打印当前结点的值,随后尝试打印左子树,打印完左子树后尝试打印右子树==,递归过程的 base case 是当某个结点为空时停止子过程的展开。这种递归尝试是由二叉树本身的结构所决定的,因为二叉树上的任意结点都可看做一棵二叉树的根结点(即使是叶子结点,也可以看做是一棵左右子树为空的二叉树根结点)。
观察先序、中序、后序三个递归方法你会发现,不同点在于打印当前结点的值这一操作的时机。你会发现==每个结点会被访问三次==:进入方法时算一次、递归处理左子树完成之后返回时算一次、递归处理右子树完成之后返回时算一次。因此在 preOrderRecursive 中将打印语句放到方法开始时就产生了先序遍历;在midOrderRecursive中,将打印语句放到递归处理左子树完成之后就产生了中序遍历;同理放在第三次访问时候打印就是后续遍历。
package cn.test;
/**
* @Author smallmartial
* @Date 2020/3/16
* @Email [email protected]
*/
public class PreInPosTraversal {
public static class Node {
public int value;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
}
/**
* 前序遍历
*
* @param head
*/
public static void preOrderRecur(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
System.out.print(head.value + " ");
preOrderRecur(head.left);
preOrderRecur(head.right);
}
/**
* 中序遍历
*
* @param head
*/
public static void inOrderRecur(Node head) {
if (head == null){
return;
}
inOrderRecur(head.left);
System.out.print(head.value + " ");
inOrderRecur(head.right);
}
/**
* 后序遍历
*
* @param head
*/
public static void posOrderRecur(Node head){
if(head == null){
return;
}
preOrderRecur(head.left);
preOrderRecur(head.right);
System.out.print(head.value + " ");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node head = new Node(5);
head.left = new Node(3);
head.right = new Node(8);
head.left.left = new Node(2);
head.left.right = new Node(4);
head.left.left.left = new Node(1);
head.right.left = new Node(7);
head.right.left.left = new Node(6);
head.right.right = new Node(10);
head.right.right.left = new Node(9);
head.right.right.right = new Node(11);
// recursive
System.out.println("==============递归版本==============");
System.out.print("pre-order: ");
preOrderRecur(head);
System.out.println();
System.out.print("in-order: ");
inOrderRecur(head);
System.out.println();
System.out.print("pos-order: ");
posOrderRecur(head);
System.out.println();
}
}(二)非递归实现
/**
*前序遍历 非递归
*/
public static void preOrderUnRecur(Node head){
System.out.println("前序:");
if(head != null){
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>();
stack.push(head);
while (!stack.isEmpty()){
head = stack.pop();
System.out.print(head.value + " ");
if(head.right != null){
stack.push(head.right);
}
if (head.left != null){
stack.push(head.left);
}
}
}
System.out.println();
}
/**
* 中序遍历
*
* @param head
*/
public static void inOrderUnRecur(Node head){
System.out.println("中序");
if(head != null){
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>();
while (!stack.isEmpty() || head != null){
if(head != null){
stack.push(head);
head = head.left;
}else {
head = stack.pop();
System.out.print(head.value + " ");
head = head.right;
}
}
}
System.out.println();
}
/**
* 后序遍历
*
* 后序遍历:先使用中左右的顺序将元素压入栈中,然后遍历栈弹出即可
*
* @param head
*/
public static void posOrderUnRecur1(Node head) {
System.out.println("后序:");
if (head != null){
Stack<Node> stack1 = new Stack<Node>();
Stack<Node> stack2 = new Stack<Node>();
stack1.push(head);
while (!stack1.isEmpty()){
head = stack1.pop();
stack2.push(head);
if (head.left != null){
stack1.push(head.left);
}
if (head.right != null){
stack1.push(head.right);
}
}
while (!stack2.isEmpty()){
System.out.print(stack2.pop().value + " ");
}
}
System.out.println();
}二、直观打印二叉树
- 在节点值两边加上特定的字符串标记来区分孩子和位置以及之间的位置关系:
- HXH:表示头结点 X;vYv:表示节点 Y 是左下方最近节点的孩子;^Z^:表示节点 Z 是左上方最近节点的孩子
- 遍历树的顺序为:右子树 -> 根 -> 左子树;
- 避免节点值长度不同影响对其,规定每个节点值长度为固定值(这里规定为 10)
package cn.test;
/**
* @Author smallmartial
* @Date 2020/3/16
* @Email [email protected]
*/
public class PrintBinaryTree {
public static class Node {
public int value;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node(int data) {
value = data;
}
}
public static void printTree(Node head) {
System.out.println("Binary Tree:");
printInOrder(head, 0, "H", 10);
System.out.println();
}
/**
* @param head :传入的节点
* @param treeHeight:层数(根节点为 0)
* @param to :表示的特定节点 H表示根节点 ^表示父亲节点在左上方 v表示父亲节点在左下方
* @param totalLength :指定每一个节点打印的宽度(总宽度)
*/
public static void printInOrder(Node head, int treeHeight, String to, int totalLength) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
// 递归遍历右子树
printInOrder(head.right, treeHeight + 1, "v", totalLength);
// 在节点值两边加上标识符
String val = to + head.value + to;
int valueLength = val.length();
// 节点值左边的空格数:(总长度 - 节点值长度)/ 2
int leftSpaceLength = (totalLength - valueLength) / 2;
// 节点值右边的空格数
int rightSpaceLength = totalLength - valueLength - leftSpaceLength;
val = getSpace(leftSpaceLength) + val + getSpace(rightSpaceLength);
// treeHeight * totalLength 为打印的节点前空格长度
System.out.println(getSpace(treeHeight * totalLength) + val);
// 递归遍历左子树
printInOrder(head.left, treeHeight + 1, "^", totalLength);
}
public static String getSpace(int num) {
String space = " ";
StringBuffer buf = new StringBuffer("");
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
buf.append(space);
}
return buf.toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node head = new Node(1);
head.left = new Node(-22);
head.right = new Node(3);
head.left.left = new Node(2);
head.right.left = new Node(55);
head.right.right = new Node(66);
head.left.left.right = new Node(7);
printTree(head);
head = new Node(1);
head.left = new Node(1);
head.right = new Node(1);
head.left.left = new Node(1);
head.right.left = new Node(1);
head.right.right = new Node(1);
head.left.left.right = new Node(1);
printTree(head);
}
}