Article Outline
TOC
Collection Outline
java基础知识学习(四)
1.容器API
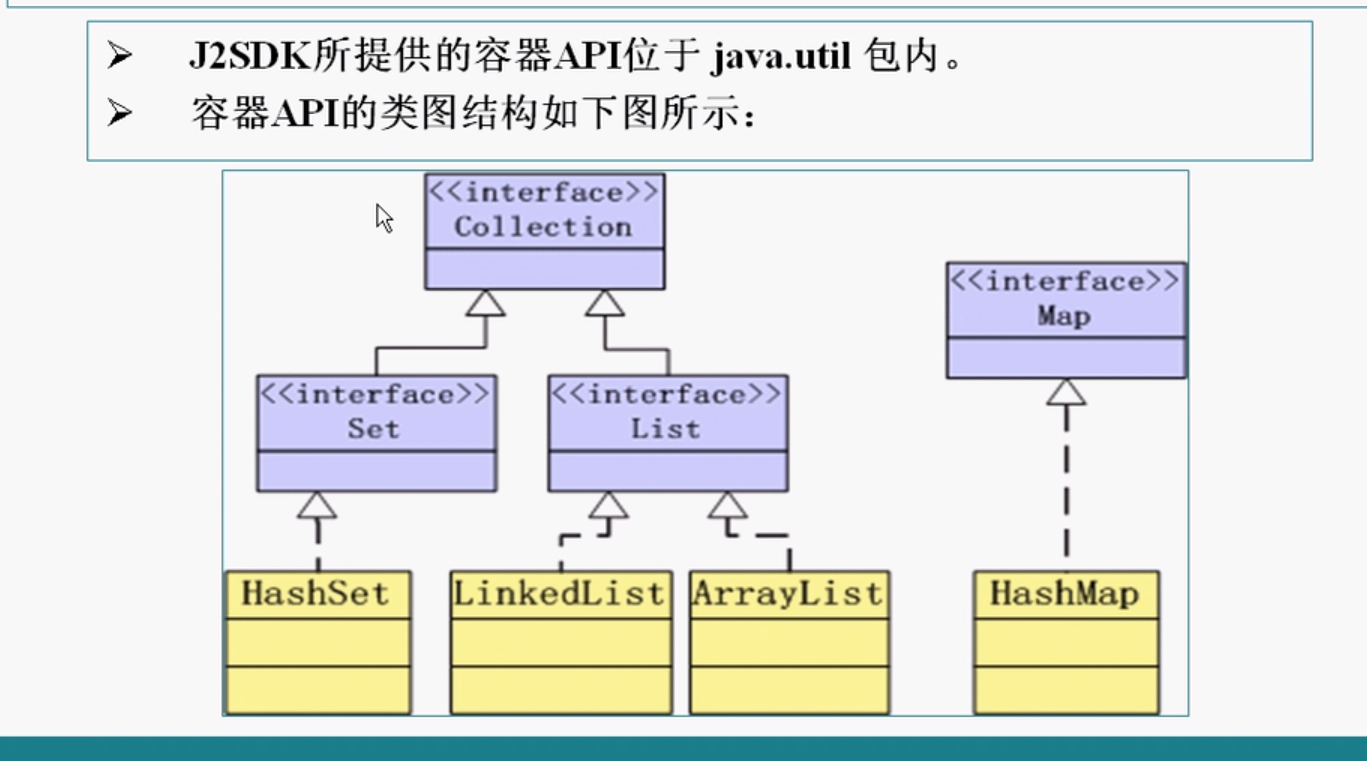
- Collection接口定义了存储一组对象的方法,其子接口的Set和List分别定义了储存方式
- Set中的数据对象没有顺序且不可以重复
- List中的数据对象有顺序且可以重复
- Map接口 定义了存储
key-value键值对的方法
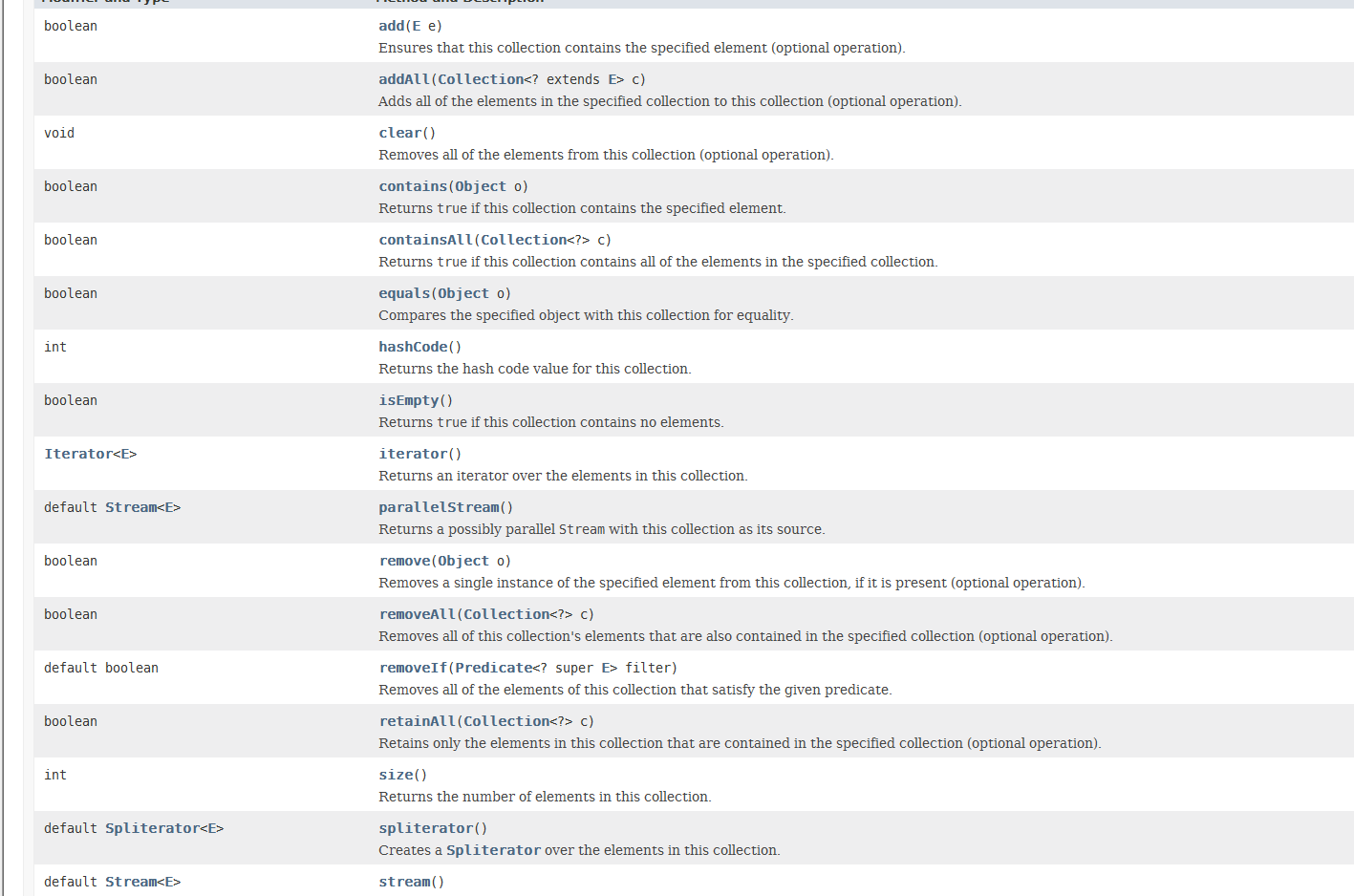
Collection接口中所定义的方法

import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
public class Test{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection c = new ArrayList<>();
//可以放入不同类型的对象
c.add("hello");
// c.add(new Name("f1","l1"));
c.add(new Integer(100));
System.out.println(c.size());
System.out.println(c);
}
}
结果:

重写equals()方法为什么要重写hashcode()方法?
- hashCode是不是重写需要看业务,开放开发人员可以重写这个方法,可能有这种情况,比如我们仅仅对比object的部分属性,就认为两者相等,而不对比其其他属性。
- 重写java object hashCode方法,是为了在一些算法中避免我们不想要的冲突和碰撞。比如其HashMap,HashSet的使用中。
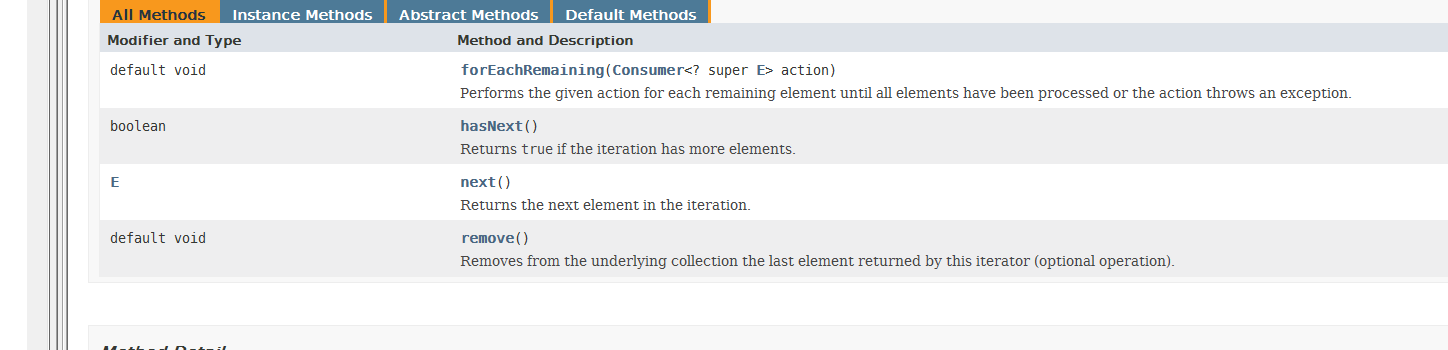
2.Iterator接口
所有实现了Collection接口的容器类中都有一个iterator方法以返回一个实现了Iterator接口的对象
Iterator对象称作为为迭代器,用以方便的实现对容器内的遍历操作
Iterator定义以下的方法:
import java.util.*;
public class Test{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
//List<String> list=new ArrayList<>();
list.add("abc");
list.add("edf");
list.add("ghi");
for(Iterator<String> it=list.iterator();it.hasNext();)
{
System.out.println(it.next());
}
}
}3.List接口
- List接口是Collection的子接口,实现List接口的容器类中元素是有序的,而且可以重复操作。
- List容器中的元素都对应一个整数型的序号记载在其容器的位置,可以根据序号存取容器中的元素。
- List容器类有ArrayList,LinkedList;
4.List常用算法
- 类·
java.util.Collections提供了一些静态方法实现了基于List容器的一些常用算法
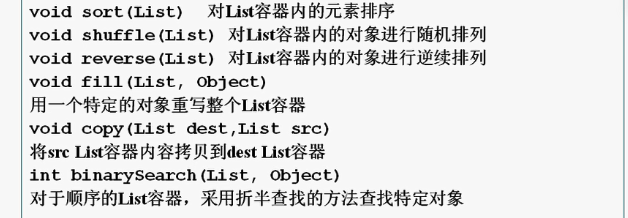
import java.util.*;
public class Test{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
List l1 = new LinkedList<>();
List l2 = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
l1.add("a" +i);
}
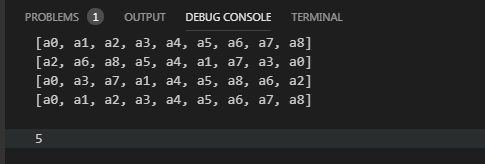
System.out.println(l1);
Collections.shuffle(l1);//随机排序
System.out.println(l1);
Collections.reverse(l1);//逆序
System.out.println(l1);
Collections.sort(l1);//排序
System.out.println(l1);
//折半查找
System.out.println(Collections.binarySearch(l1, "a5"));
}
}运行结果:
5.Comparable接口
- 所有可以
排序的类都实现了java.lang.Comparable接口,Comparable接口中只有一个方法:public int compareTo(Object obj);- 返回 0 表示this == obj
- 返回正数表示 this > obj
- 返回负数表示 this < obj
- 实现了Compareable接口的类通过实现compareTo方法而确定该类的排序方式
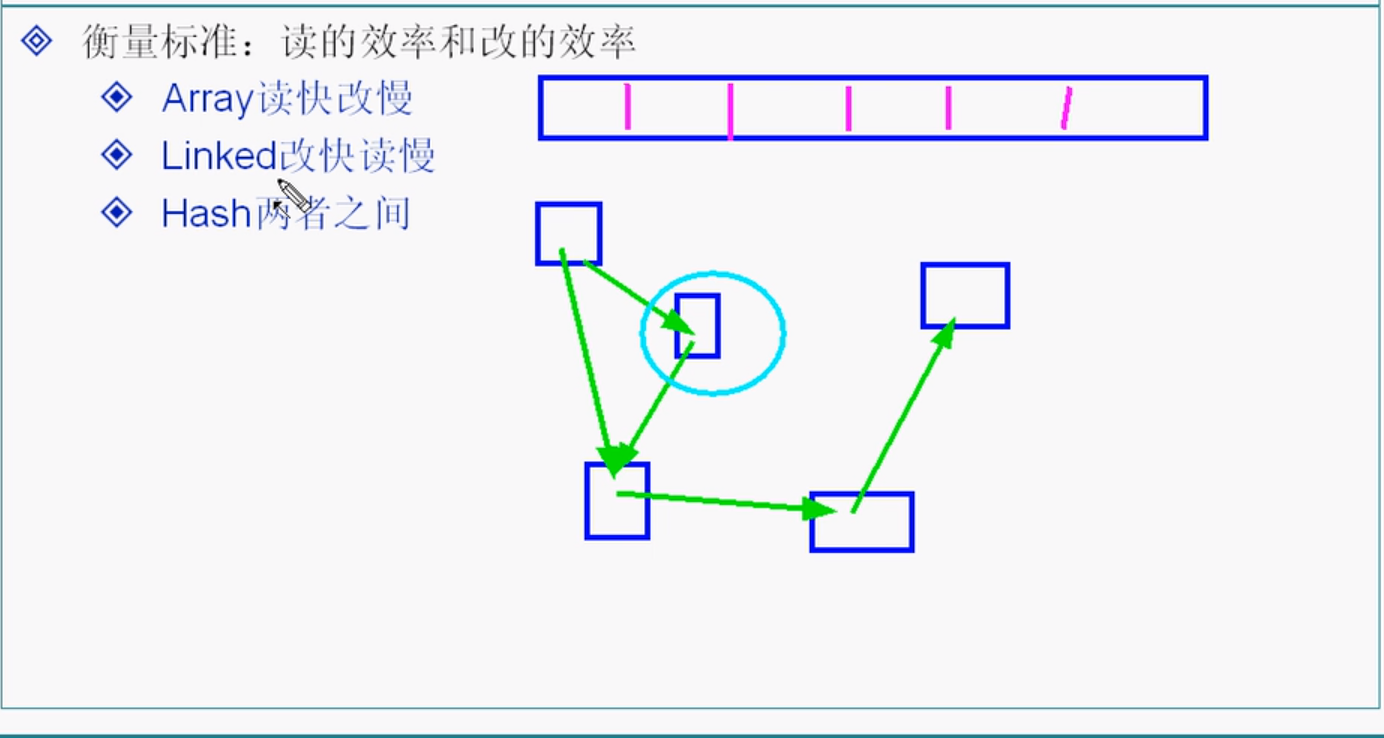
6.数据结构读写效率比较
7.Map接口
实现map接口的类用来存储键值对
Map接口中实现类有HashMap和TreeMap等
Map类中存储键值对通过键来标识,所以键值不能重复
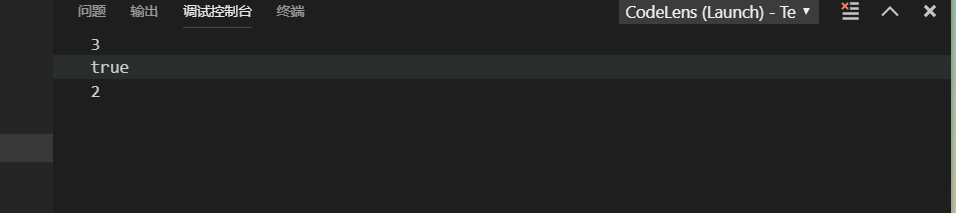
import java.util.*; public class Test{ public static void main(String[] args) { Map m1 = new HashMap(); Map m2 = new TreeMap(); m1.put("one",1); m1.put("two",2); m1.put("three",3); m2.put("A",1); m2.put("B",2); System.out.println(m1.size()); System.out.println(m1.containsKey("one")); if(m1.containsKey("two")){ int i = (Integer) m1.get("two"); System.out.println(i); } } }结果:
8.泛型

import java.util.*;
public class Test{
public static void main(String[] args) {
//改写为泛型
Map<String, Integer> m1 = new HashMap<String,Integer>();
Map m2 = new TreeMap();
m1.put("one",1);
m1.put("two",2);
m1.put("three",3);
m2.put("A",1);
m2.put("B",2);
System.out.println(m1.size());
System.out.println(m1.containsKey("one"));
if(m1.containsKey("two")){
//int i = (Integer) m1.get("two");
int i = m1.get("two");
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
总结