通过简单计数器学习Vuex
Vuex是啥❓
Vuex 是一个专为 Vue.js 应用程序开发的状态管理模式。它采用集中式存储管理应用的所有组件的状态,并以相应的规则保证状态以一种可预测的方式发生变化。简单来说就像一个超级商店里面有许多你需要的的东西。每一个 Vuex 应用的核心就是 store(仓库)。“store”基本上就是一个容器
Vuex使用单一状态🌲
Vuex项目结构
├── index.html
├── main.js
├── api
│ └── ... # 抽取出API请求
├── components
│ ├── App.vue
│ └── ...
└── store
├── index.js # 我们组装模块并导出 store 的地方
├── actions.js # 根级别的 action
├── mutations.js # 根级别的 mutation
└── modules
├── cart.js # 购物车模块
└── products.js # 产品模块重点词汇 🏁
state(状态/steit/)驱动应用的数据源;每个应用将仅仅包含一个 store 实例
mutation 改变 你不能直接改变 store 中的状态。改变 store 中的状态的唯一途径就是显式地提交 (commit) 状态改变逻辑写在这里面
getters 获取打包处理也是一个计算函数
commit 指派修改 例:store.commit('item') 通过指派任务触发mutation中的事件
modules 模块
methods 方法
view,以声明方式将 state 映射到视图;
actions,响应在 view 上的用户输入导致的状态变化。复杂的业务逻辑写在这
computed 计算属性
dispatch 分派
mapstate 辅助函数 为了减少声明帮我们生成计算属性
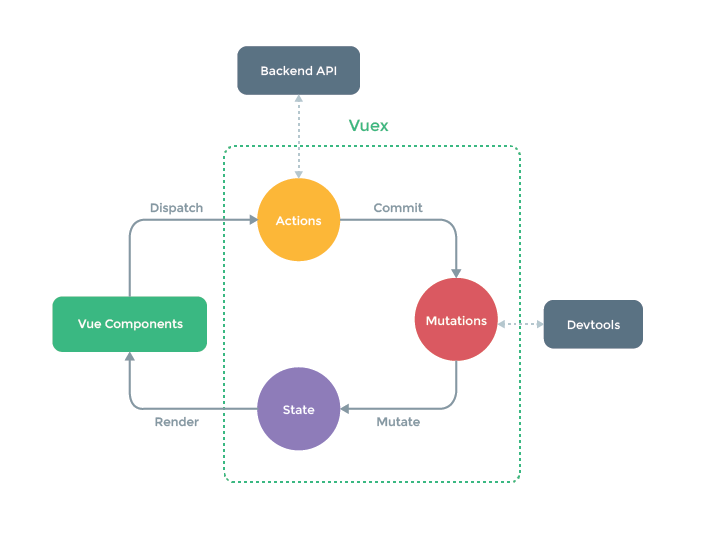
Vuex 是专门为 Vue.js 设计的状态管理库,以利用 Vue.js 的细粒度数据响应机制来进行高效的状态更新。
什么情况使用??不用想肯定是麻烦大型的单页应用才使用吧要不然要你何用😂直接使用store模式就👌了
起步
有木有熟悉的味道??? 我们已经见过很多次了import将下载好的vuex引入并use使用它
//新建store文件夹📁存放//在store.js中引入
import Vue from 'vue';
import Vuex from 'vuex';
import Index from './index'
Vue.use(Vuex);main.js中引入以下文件
import Vue from 'vue';
import App from './App.vue';
import router from './router';
import store from './store/store';
new Vue({
router,
store,
render: h => h(App),
}).$mount('#app');
首先我们需要知道我们需要在页面上使用字符模版{{ count }}把内容渲染出去
创建store
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state:{
count:0
},
mutations:{
increment(state){
state.count ++
},
decrement(state){
state.count --
}
}
})好的我们创建好这个以后就可以开始使用了
为了能看见它能➕能➖我们是否还需要两个button来控制一下呢?
当然我们需要所以我们在组件helloworld🀄️添加上两个按键一个是increment另一个是decrement
<template>
<div class="hello">
<button @click="increment">+</button>
<button @click="decrement">-</button>
</div>
</template>完成了吗?不我们还差最后一步工作就是在组件中引用这两个方法
export default {
increment(){
//可以不加也能调用
//this.$store.commit('increment')
//this.increment
// this.myIncrement
},
decrement(){
//this.$store.commit('decrement')
//this.decrement
// this.myDecrement
}
}上面四种方法都可以做到控制加减变化我们可以根据情况来具体使用
接着我们介绍一下Action
- Action 提交的是 mutation,而不是直接变更状态。
- Action 可以包含任意异步操作。
我们注册一个
actions: {
myIncrease(context){
context.commit('increment')
},
myDecrement(context){
context.commit('decrement')
},
},我们可以调用context.getters提交
我们可以使用action做简单的逻辑操作
//helloworl.vue中引入
//创建组件方法分发 action
//传入两种方法
methods:{
...mapActions(['myIncrement','myDecrement'])
},在组件中分发action详解
import { mapActions } from 'vuex'
export default {
// ...
methods: {
...mapActions([
'increment', // 将 `this.increment()` 映射为 `this.$store.dispatch('increment')`
// `mapActions` 也支持载荷:
'incrementBy' // 将 `this.incrementBy(amount)` 映射为 `this.$store.dispatch('incrementBy', amount)`
]),
...mapActions({
add: 'increment' // 将 `this.add()` 映射为 `this.$store.dispatch('increment')`
})
}
}还有一个getters放到后面因为使用比较简洁我们注册一个getters
//在store中注册
getters:{
myCount(state){
return `hi ~ ${state.count}`
}
},
// 在app.vue中注入
import {mapGetters} from 'vuex'
export default {
computed:{
...mapGetters(['myCount'])
}
}Modeule模块
当内容相当多的时候代码会相当臃肿复杂所以我们需要将它插分为模块
官方实例
const moduleA = {
state: { ... },
mutations: { ... },
actions: { ... },
getters: { ... }
}
const store = new Vuex.Store({
modules: {
a
}
})
store.state.a // -> moduleA 的状态单独页面引入
import Index from './index'
Vue.use(Vuex);
const store = new Vuex.Store({
modules:{
Index
}
})
export default store还有最后{{count}} 的指向问题就是分离模块后指向错所以不能得到正确数据无法渲染所以我们需要为count重新指向
computed:{
...mapState({
count: state => {
return state.Index.count
},
}),
}更多补充
mapState
为组件创建计算属性以返回 Vuex store 中的状态。
mapGetters
为组件创建计算属性以返回 getter 的返回值。
mapActions
创建组件方法分发 action。
mapMutations
创建组件方法提交 mutation